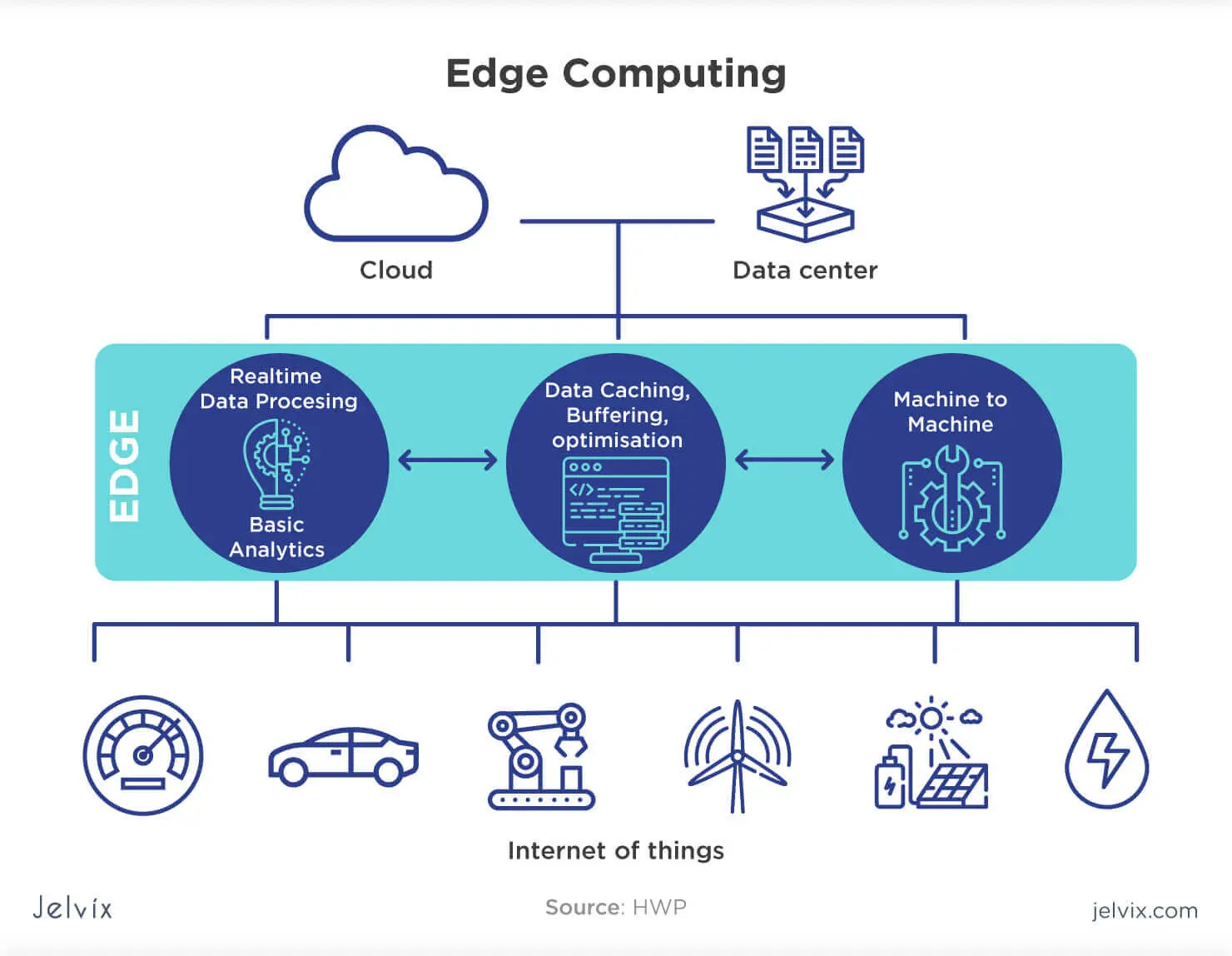
The emergence of serverless platforms plays a crucial role in the adoption of edge computing. Serverless platforms eliminate the complexities of infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus on building and deploying their applications. With serverless computing, the cloud provider automatically handles scaling, provisioning, and resource management. Developers no longer need to worry about managing servers, making deployment easier and more efficient.
In addition to simplifying deployment, serverless computing helps to reduce costs. Traditional serverbased models often require businesses to pay for a fixed amount of server capacity, regardless of whether it is fully utilized. On the other hand, serverless computing operates on a payasyougo model. Users are only charged for the resources consumed during application execution, leading to more efficient cost management.
Scalability is another key benefit of serverless platforms. With dynamic resource allocation, serverless platforms automatically scale resources based on demand. This ensures that applications can handle varying levels of traffic without the need for manual intervention. For example, if a web application experiences a traffic spike, the serverless infrastructure will scale up to meet the demand and scale down when the traffic decreases. This level of flexibility is ideal for modern web applications, which often experience fluctuating usage patterns.
However, while serverless offers many advantages, it’s important to consider some potential pitfalls. One key challenge is managing cold start latency. Cold starts occur when serverless functions are triggered for the first time after being idle for a period, causing a delay in response time. While edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the user, serverless functions must be optimized to minimize cold start issues. Additionally, efficient resource allocation and monitoring are essential to ensure that the system remains responsive and costeffective.